
栈 线性数据结构的一种 可以理解为操作受限的线性表
栈的特点 先入后出 (可以想象一下装羽毛球的球筒,先放进去的在最底下)
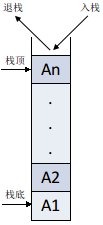
栈的表尾端称为栈顶,表头称为栈底,插入和删除都只能在栈顶操作,插入操作称为入栈,弹出操作称为出栈。
下面是栈的顺序存储结构的C实现代码
#include#include #define TRUE 1#define FALSE 0#define OK 1#define ERROR 0#define OVERFLOW -2#define INIT_SIZE 20#define INCREMENT_SIZE 5typedef int SElemType;typedef int Status;/* * 存储结构 */typedef struct{ SElemType *base; //栈尾指针 SElemType *top; //栈顶指针 int size; //栈的大小}SqStack;/* * 初始化栈 */ Status InitStack(SqStack *S){ S->base = (SElemType*) malloc(INIT_SIZE * sizeof(SElemType)); if (!S->base) { exit(OVERFLOW); } S->top = S->base; S->size = INIT_SIZE; return OK;}/* * 销毁栈 */Status DestroyStack(SqStack *S){ free(S->base); S->base = NULL; S->top = NULL; S->size = 0; return OK;}/* * 清空栈 */Status ClearStack(SqStack *S){ S->top = S->base; return OK;}/* * 判断栈是否为空 */Status IsEmpty(SqStack S){ if (S.top == S.base) { return TRUE; } else return FALSE;}/* * 获取栈的长度 */int GetLength(SqStack S){ return (S.top - S.base) / sizeof(SElemType);}/* * 获取栈顶元素 */Status GetTop(SqStack S, SElemType *e){ if (S.top > S.base) { *e = *(S.top - sizeof(SElemType)); return OK; } else { return ERROR; }}/* * 压栈 */Status Push(SqStack *S, SElemType e){ if ((S->top - S->base) / sizeof(SElemType) >= S->size) { S->base = (SElemType*) realloc(S->base, (S->size + INCREMENT_SIZE) * sizeof(SElemType)); if (!S->base) { exit(OVERFLOW); } S->top = S->base + S->size * sizeof(SElemType); S->size += INCREMENT_SIZE; } *S->top = e; S->top += sizeof(SElemType); return OK;}/* * 退栈 */Status Pop(SqStack *S, SElemType *e){ if (S->top == S->base) { return ERROR; } S->top -= sizeof(SElemType); *e = *S->top; return OK;}/* * 访问元素 */void visit(SElemType e){ printf("%d ", e);}/* * 遍历栈 */Status TraverseStack(SqStack S, void (*visit)(SElemType)){ while (S.top > S.base) { visit(*S.base); S.base += sizeof(SElemType); } return OK;}int main(){ SqStack S; if (InitStack(&S)) { SElemType e; int i; printf("init_success\n"); if (IsEmpty(S)) { printf("Stack is empty\n"); } for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Push(&S, i); } GetTop(S, &e); printf("The first element is %d\n", e); printf("length is %d\n", GetLength(S)); Pop(&S, &e); printf("Pop element is %d\n", e); TraverseStack(S, *visit); if (DestroyStack(&S)) { printf("\ndestroy_success\n"); } }}